Film-laminated metal materials are very common, such as metal doors and windows, elevators, kitchen utensils, etc. In order to maintain the surface smoothness and integrity, metal materials are usually laminated with films to avoid scratches during transport.
Known as a metal cutting expert, people may ask, can a fiber laser cutting machine cut film laminated metal sheet?
The answer is that a fiber laser can cut laminated metal sheets, but there are certain difficulties.
This post will share some tips.
Table of Contents
Difficulties in Film Laminated Metal Sheet Cutting with a Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
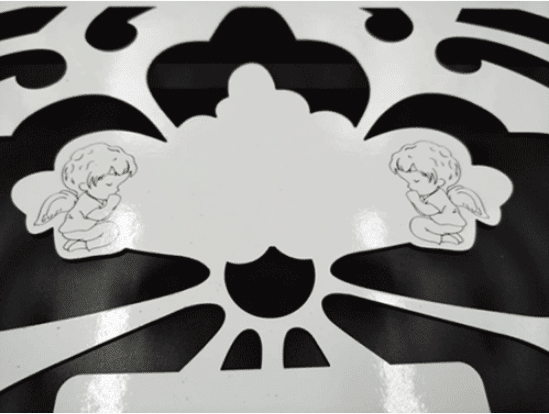

- Since the fiber laser has a relatively short wavelength, only 1.06um, it is difficult to be absorbed by non-metallic materials. When cutting film-laminated stainless steel, slags, incomplete cutting, high reflection alarm phenomena frequently occur, which has a great impact on cutting quality and normal production.
- In order to melt the surface film, it is necessary to utilize the reflected heat of the laser on the metal plates. If the power is too low, the film cannot be cut through; if the power is too high, the surface of the plate is easily damaged.
- A single cut of the laminated metal is very unstable, and the surface film is easily blown up.
Then how do we cut film-laminated metal sheet with fiber laser cutting machine?
Since the film-laminated metal sheets are further divided into single-sided film-laminated metal sheets and double-sided film-laminated metal sheets. We will discuss the film-laminated metal sheet cutting respectively.
Single-sided Film-laminated Metal Sheet Cutting

When cutting single-sided film-laminated metal sheets, such as the brushed or mirrored stainless steel, in order to avoid film damaging, the side with the film is usually cut with facing upward, and the side without the film is facing downward. Because of the side of the film is facing down, the residue splashed by the laser cutter may stick to the film due to thermal influence, which will make the film surface rough. Meanwhile, it is difficult to cool down the film after cutting and to remove the dross attached to it. Therefore, it is recommended to cut the surface with the film first.
The cutting process is as follows:
Lower the power and keep the distance between the laser head and surface of the material at about 10 mm. Then, burn the protective film in the cutting path, and perform cutting afterward.
Note: It is better to install a pneumatic device on the backside of the metal sheet to avoid scratches by the sharpen sawtooth support worktable.
Double-sided Film-laminated Metal Sheet Cutting
Difficulties in the cutting of double-sided film-laminated metal sheets
We know that the fiber laser cutting head can only perform cutting from the top to bottom. Although the laser will have no big effect on the protective film on the top surface of metal sheet during the cutting process, the cutting residues generated during the cutting process may not fall down due to the laminated film on the back of the sheet. These residues will directly affect the cutting effect of the sheet, resulting in incomplete cutting of sheet or generation of large burrs after cutting. However, if the protective film under the sheet is completely torn off, the back of the sheet is easily scratched.
Is there any way to not tear off the whole film under the sheet and make sure the protective film does not affect the cutting? The answer lies in the cutting position of the laser cutting.
Metal laser cutting machine solution
The protective film on the bottom of the sheet does not affect the cutting quality. Only the protective film on the bottom of the cutting position affects the cutting quality. So, it is only necessary to remove the protective film on the bottom surface of the sheet cutting position.
Therefore, for double-sided cutting, we can use the function of laser etching. First, find out the actual cutting position on the sheet, then tear off the protective film at the cutting position, turn the sheet over, and perform the cutting.
This requires the following steps:
- Draw an auxiliary cut chart that matches the actual cut chart. The specific method is to mirror the actual cut image, and you can directly get the auxiliary cut chart.
- Calculate the position and maximum offset of the film to be removed. Theoretically, the protective film of the cutting position is etched away by laser etching on the upper surface of the sheet by using an auxiliary cutting pattern, you can cut directly. However, in the actual cutting process, due to the influence of laser positioning error and sheet shape error, the cutting position of the front and back of the sheet is impossible to coincide with. Therefore, the accurate offset should be measured during the front etching, and the protective film at the offset position can be torn off.
- Draw cutting drawings and auxiliary cutting drawings. The cutting drawings can be drawn directly according to the shape of the workpiece. The auxiliary cutting drawings are mirrored, and then the actual cutting drawings are mirrored, and then the offset is made with the set error value.
- Perform laser cutting drawing typesetting. It is necessary to first typeset the auxiliary cutting drawings. Secondly, make the layout of the auxiliary cut image mirrored, remove the etched line, keep only the actual cut image.
- Perform laser cutting. First, do a good job of etching, and then tear off the protective film at the laser cut position. After the protective film is torn off, the steel plate is turned over, and then the workpiece is cut.
How to Avoid Metal Sheet Film Peeling During Laser Cutting

Although, fiber laser cutting machine can perform cutting on film-laminated metal sheets, sometimes film peeling may occur during the cutting process.
If the film peeling occurs, it is normally related to the cutting gas. During the cutting process, the gas keeps blowing on cutting surface and easily enters into the protective film, resulting in film peeling. The occurrence of film peeling may be due to laser processing conditions and the protective film itself. Let’s take a closer look.
Check processing conditions
When the melting range is large, the adhesive strength of the protective film is lowered, thereby leaving a hidden danger for the peeling of the film.
When cutting the protective film, the intensity of the laser beam pattern at the cutting edge should be sharply distributed, and be careful not to cause the laser to be disordered. Increase the speed to reduce the thermal influence of the laser on the protective film. In addition, the sharp corners in the machined shape or the small hole are also prone to peeling, and it is necessary to modify the shape by setting R or the like.
Use professional laser cutting film
If the adhesion of the film itself is low or the quality is poor, the thermal effect during processing will cause the film to shrink due to heat, thereby causing gaps. In this case, the cutting assist gas may invade the surface of the material and the film. In the meantime, a large area of the film peeling is formed.
Good film permits protected sheet metal to be laser cut in a single run and reduces laser-cutting time and will maintain surface integrity while parts are being cut.
Furthermore, practices from the metal fabricators prove that black-on-back film gave better results than a white-backed film, you can refer more details at https://www.industrial-lasers.com/cutting/article/16485574/fiber-laser-cutting-thin-stainless-steel).
In conclusion, the above is the whole content of the film-laminated metal sheet cutting with a fiber laser cutting machine. Hope this post is helpful to you. If you have any questions, please send us an email and we will try our best to serve you.





